Cell Biology
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cell
- Animal Cell and Plant Cell
- Specialized Plant Cells
- Specialized Animal Cells
- Microscopy
- Culturing Microorganisms
- Cell Division: Mitosis
- Stem Cells
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active Transport
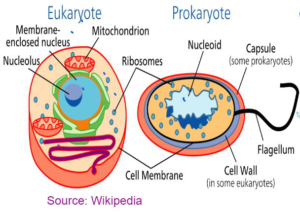
Eukaryotic Cells – Plants and Animals Prokaryotic Cells – Bacteria
| EUKARYOTIC | PROKARYOTIC |
| Nucleus is present. | Nucleus is absent. |
| All membrane bound organelles are present | Membrane bound organelles are absent. |
| DNA is enclosed in the nucleus | DNA lies naked in the cytoplasm. |
| They are multicellular | They are mostly unicellular |
| DNA is linear | DNA Is circular |
| Ribosomes are big | Ribosomes are small |
| They are big cells | They are small cells. |
| Example: Plants and Animals | Example: Bacterial Cell |
Animal Cells
NUCLEUS
- It is the brain of the cell
- It controls the activities of the cells
- It contains DNA which holds our genetic information.
RIBOSOMES
- It is the site for protein synthesis.
- They are involved in making of proteins and enzymes required by the cell
CYTOPLASM
- Jelly like fluid which fills the cell.
- It is the site where all the chemical reactions of the cells take place as it contains all the major enzymes
CELL MEMBRANE
- It the membrane that surrounds the cells
- It controls what goes in and out of the cell.
MITOCHONDRIA
- It is the powerhouse of the cell
- It produced energy for the cell as it is the site for aerobic respiration
Banner 3
Plant Cell
PERMANENT VACUOLE
- It is filled with cell sap.
- It gives rigidity to the cells and makes the cell turgid
CELL WALL
- Made up of cellulose.
- It is the layer outside of the cell membrane
- It supports the plant and maintain its shape.
CHLOROPLAST
- It is the site for photosynthesis
- It contains a green pigment, chlorophyll which absorbs light and prepared food.
Plant versus Animal Cell
| ORGANELLE | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| Nucleus | Present | Present |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present | Present |
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Permanent Vacuole | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplast | Present | Absent |
Bacterial Cell
Cell Wall
- No cellulosic
- made up of peptidoglycan
Circular DNA
- No nucleus
- Single DNA loop found naked in the cytoplasm
Plasmid
- Extra chromosomal materials
- They are in the form of small rings
- They give special properties to bacteria like antibiotic resistance
Pilli
- Hair like structures
- Found on the surface
- That helps bacteria to reproduce
Capsule
- Slime layer
- that protects the bacteria
Flagellum
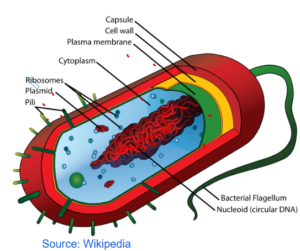
- Tail like structure
- Helps the bacteria to move.
Banner 5 GCSE CELL BIOLOGY
Download the Printable PDF of these notes here :-
Download --> Download
Restricted download
BACTERIAL VERSUS PLANT VERSUS ANIMAL CELLS
SPECIALISED ANIMAL CELLS
Special cells which have some extra features that allows them to perform specific functions
NERVE CELL
Function is to send electrical impusles round the body
- Dendrites – They are hair like structures that receives the impulses
- Axon – Long stalk the transmits the nerve impulses
- Synapse – They transmit impulses from one neurone to another
MUSCLE CELL
- Functions is to contract to bring about the movement of different parts of the body
- They are made up of special fibres which helps them to contract and relax
- Contain special proteins that allows them to contract and relax
- They have loads of mitochondria which provides them energy to contract
- They can store special storage carbohydrate called glycogen which acts as fuel for the muscles
SPERM CELL
Functions is to swim to the egg and fertilize it
- Flagella – Helps it to swim to large distances
- Mitochondria – Provides Energy to swim
- Nucleus – Contains genetic information
- Acrosome – Contains Hydrolytic enzyme to break the egg wall and penetrate inside the egg to fuse with the egg nucleus
Specialized Plant Cells
MICROSCOPES
Are the devices that use to see the cells which we cannot see by our naked eye.
MAGNIFICATION
The property of the microscope to enlarge the object.
RESOLUTION
The property of the microscope to distinguish between two closed placed objects. Baneer 6
Light and Electron Microscopes
| LI&HT MICROSCOPES | ELECTRON MICROSCOPES |
| Uses beam of light to focus on the object. | Use beam of electron.to focus on the object. |
| It is easy to handle | It is not easy to handle |
| It is small and compact | It is big and non portable |
| It does not require much expertise to handle | It requires proper training to handle |
| It can view the live samples | Samples have to be dead |
| No special sample preparations are required | Special sample preparations ace required |
| Lower resolving power – 0.2μm | Greater resolving power 0.5nm |
| Small magnifying power – x1000 -1500 | Greater magnifying power – x100000 |
| Can form colour images | Form 2D or 3D black and white images |
MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCE IN AND OUT OF THE CELLS
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration.
- Particles move against the concentration gradient.
- It requires energy.
- Cells involved in active transport should have lots of mitochondria
PASSIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of particles from the region of high concentration to a low concentration.
- Particles move along the concentration gradient.
- It does not require energy
- Having numerous mitochondria is not a requirement
DIFFUSION
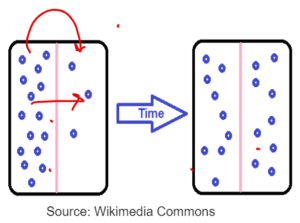
- It the net movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
- It is passive process
- It happens along the concentration gradient
- No use of energy.
Banner 9
FACTORS AFFECTING DIFFUSION
SURFACE AREA
- Greater the surface area greater is the rate of diffusion as particle will get more room for movement.
- All the exchange surfaces have greater surface area like root cells has root hairs and intestine cells has villi.
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT
- Greater the difference in concentration in the two region greater is the rate of diffusion.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain steepest concentration gradient
- Like root cells are closed to xylem and Villi has rich blood supply.
DIFFUSION DISTANCE
- Smaller the diffusion distance greater is the rate of diffusion as the particles have to travel a smaller distance.
- All the exchange surfaces maintain a smaller diffusion distance by being one cell thick.
TEMPERATURE
- Greater the temperature greater is the rate of diffusion as particles will get more kinetic energy for movement
- Rate of Diffusion = Surface area x Concentration gradient/Diffusion Distance
OSMOSIS – Special Case of Diffusion
Osmosis is the net movement of water particles from the region of high concentration of water particles to low concentration of water particles across a semi permeable membrane. Movement of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi permeable membrane. Special Case:
- It is the diffusion of only water molecules
- It required a semi permeable or partially membrane
- Membrane that allows only specific molecules to pass through like water.
OSMOSIS IN PLANTS
- Hypertonic – The outer solution has a less concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Isotonic – The outer solution has same concentration of water than inside the cell.
- Hypotonic – The outer solution has a greater concentration of water than inside the cell.
Plasmolyzed – The water moves out of the cells due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water inside the cell than outside. The cell membrane recetes from the cell wall Flaccid – There will no net water movement so no pressure on the cell. It will be flaccid Turgid – The water moves into the cell due to osmosis due to higher concentration of water outside the cell. The water will create pressure called turgor pressure on the cell wall making cell rigid and turgid.
Osmosis in Animals
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
- Movement of substances from the region of low concentration to a region of higher concentration with the use of energy.
- Dependent on respiration as it requires energy. So the cells involved in active transport has lots of mitochondria.
- In Plants water and minerals are absorbed by active transport to absorb maximum of water and minerals.
- In animals, the digested food gets absorbed into the blood by active transport to ensure maximum absorption
- Salt glands are present in some marine organisms which removes the salt by active transport.
CELL CYCLE
Interphase –
- It is the longest phase of the cell cycle
- The cell grows in size and prepares all the proteins and enzymes needed for division.
- Replication of DNA where DNA duplicates its content.
Mitosis
- It is the division of the nucleus in which parent cell splits into two daughter nuclei containing same number of chromsomes as the parent cell.
Cytokinesis
- It is the division of the cytoplasm which .takes place after the division of the nucleus.
Mitosis
- It is the type of cell division in which a parent nucleus divides to form two daughter nuclei with exactly the same number of chromomes as that of the parent nucleus.
- The daughter cells produced are genetically identical to the parent and are clones.
- This division is important for growth, regneration and repair.
- Mitosis is also important in asexual reproduction.
CELL DIFFERENTIATION
- It is the process by which cell becomes specialised to perform a specific function.
- Male Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Sperm (male gamete)
- Female Parent (23 pairs of chromosomes) Meiosis
Ovum (Female gamete)
Animal Differentiation
- In animals majority of the cells are differentiated at an early stage and different cells have specific functions like nerve cell, muscle cells.
- Adult stem cells replaced the old and worn out cells in human but adult stem cells have limited specialization power
- Majority of the differentiation is permanent
Plant Differentiation
- Plants are the storehouse of stem cells
- Root meristems and shoot meristems are the parts of actively growing part of the cells which contains stem cells.
- The plants can be cloned easily as it has many undifferentiate cells and differentiation is not permanent.
STEM CELLS
- Undifferentiate mass of cells that can differentiate into any cell type are known as stem cells.
- Sources of Stem Cells : Embryo, left over remains of the embryo and the umbilical chord are the sources of embryonic stem cells.
- Bone marrow is the source of adult stem cells.
- Can solve the rejection problem if the transplanted organ is made from the person’s own stem cells.
- Can be possible cure of neuro-degenerative diseases
- Can be the potential cure of diabetes.
- Therapeutic cloning.
- Organ damage problem
ISSUES AGAINST STEM CELLS
- It can lead to cancer as the stem cells are rapidly dividing.
- The stem cells can be contaminated and can cause unwanted diseases to the patient.
- Research is still slow and expensive
- Research happens on aborted embryos which is considered as a potential source of life and many religions have ethical concerns against it.
- The knowledge of the genes switched on and off using differentiation is still incomplete.
KEY TERMS.
- Cells – Basic structural and functional unit of the living organism.
- Mitochondria —The cell organelle which is the site of aerobic respiratiom
- Nucleus — The cell organelle which controls the activities of the cell
- Cytoplasm –The jelly like fluid which fills the cell and contains enzymes for chemical reactions.
- Ribosomes — The cell organelle which is the site for protein synthesis
- Prokaryotic – Cell The primitive cell without nucleus or membrane bound organelles.
- Eukaryotic cell —The advanced cell type with nucleus and membrane bound organelle
- Cell Wall— The outer layer of the plant cell which provide shape and support
- Cell Membrane – The layer that controls what goes in and out of the cell.
- Vacuole – Organelle present in plant cell which has cell sap and make the cell turgid.
- Microscopes – Devices that is used to see the object which are not visible by a naked
- Resolution – Ability to distinguish between closely placed objects.
- Magnification — Ability to enlarge an object
- Xylem – Transport tissue in plants that transports water and minerals.
- Phloem – Transport tissue in plants that transports food
- Diffusion – Movement of substance from a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
- Osmosis — Movement of water from high concentration of water to low concentration of water across semi permeable membrane
- Plasmolysis— Shrinking of plant cell when placed in hypertonic solution.
- Turgid — Fully swollen cell which has gained water by osmosis.
- Flaccid— soft cell due to no net movement of water.
- Mitosis — Cell division that produces identical daughter cells.
- Differentiation – Cell specialization
- Stem Cells – Undifferentiated mass of cells that can specialize to any cell type
- Therapeutic cloning — Using adult stem cells to produce embryonic stem cells and differentiating them to produce a required cell type Banner 12 Disclaimer:I have tried my level best to cover the maximum of your specification. But this is not the alternative to the textbook. You should cover the specification or the textbook thoroughly. This is the quick revision to help you cover the gist of everything. In case you spot any errors then do let us know and we will rectify it.References:BBC BitesizeWikipediaWikimedia CommonsImage Source:WikipediaWikimedia Commons Flickr Pixabay
Question by Topic
Make sure you have watched the above videos and are familiar with the key definations before trying these questions. It is also good to time yourself while doing these questions so that you can work on the speed as well.
Cell Biology
B1- Cell Structure And Transport
- Cell Structure 1 MS
- Cell Structure 1 QP
- Cell Structure 2 MS
- Cell Structure 2 QP
- Cell Structure 3 MS
- Cell Structure 3 QP
- Transport in Cells 1 MS
- Transport in Cells 1 QP
- Transport in Cells 2 MS
- Transport in Cells 2 QP
- Transport in Cells 3 MS
- Transport in Cells 3 QP
B2 -Cell Division
- Cell Division 1 MS
- Cell Division 1 QP
- Cell Division 2 MS
- Cell Division 2 QP
- Cell Division 3 MS
- Cell Division 3 QP




